Docking
Ultrasonic Sensors on the bot
On the rear side of the bot, you can find 2 ultrasonic sensors. Here is the representation of it.
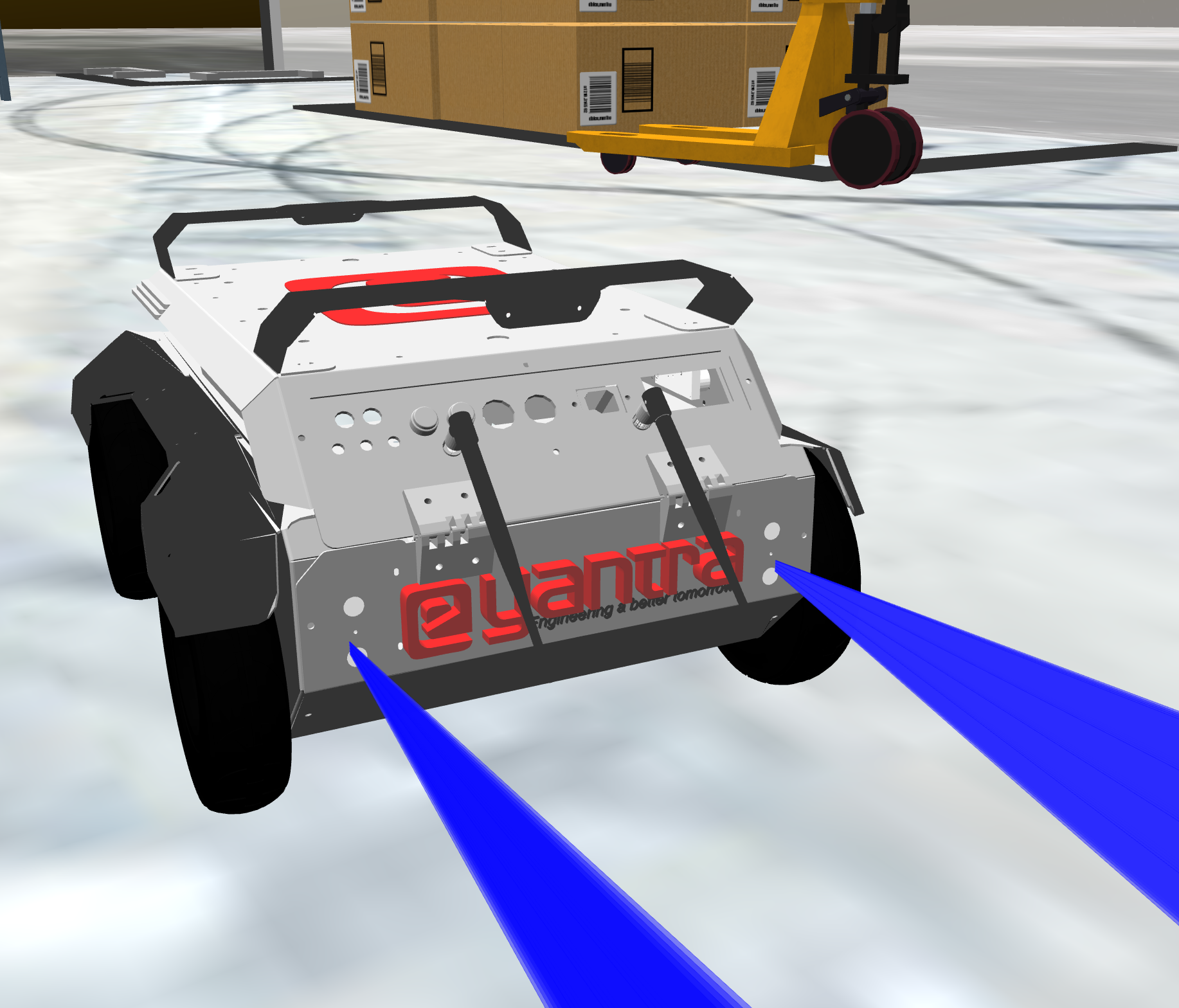

The ros2 topic for this sensors are /ultrasonic_rl/scan for left and
/ultrasonic_rr/scan for right, using msg type sensor_msgs/msg/Range
- To enable or disable the visualization of the sensors you can go to
ebot_description/models/ebot/ebot.gazebo- Under ebot.gazebo, go to the Ultrasonic section
<!-- Ultrasonic --> <xacro:macro name="ultrasonic_sensor" params="name"> <gazebo reference="${name}"> <sensor type="ray" name="${name}"> <pose>0 0 0 0 0 0</pose> <visualize>true</visualize> ```
Concept
Consider a scenario like below,
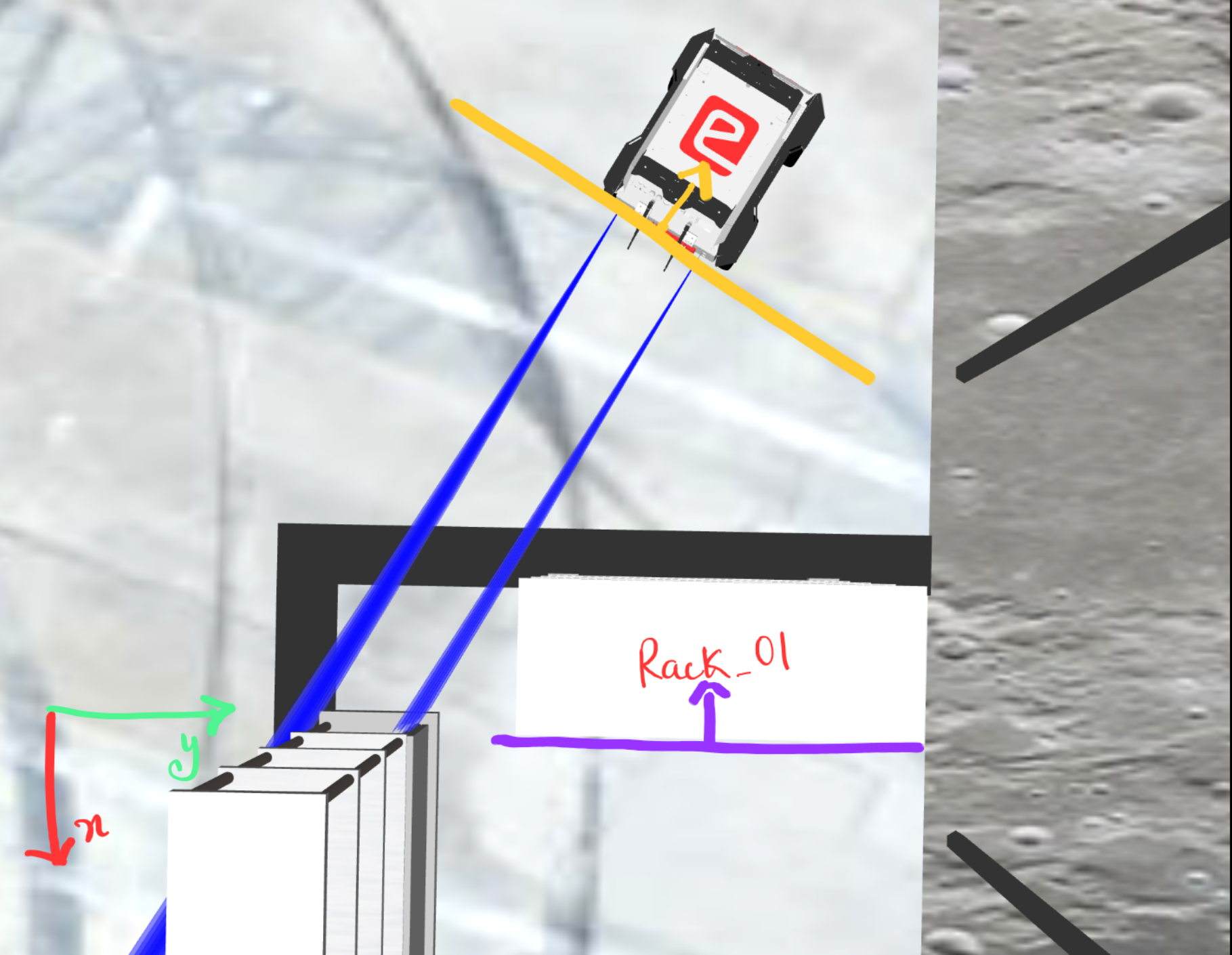
here you can see we can first align the orientation of the bot wrt the rack,
-
Aligning orientation: We can do this using the
IMUsensor directly or usingUltrasonicsensors reading and doing simple coordinate geometry.- Using IMU directly, the orientation data of the ebot can be directly accessed using topic
/imuand msg-typesensor_msgs/msg/Imu
Doing
ros2 topic echo /imu --onceheader: stamp: sec: 823 nanosec: 847000000 frame_id: ebot_base_link orientation: x: 0.000953526911620944 y: 0.00021382570450593477 z: -0.00048188256696325623 w: 0.9999994064269182Angles are in
quaternion, GOOGLE it !!!Here you can see, that we get the orientation of the ebot and we already know the orientation of the rack. Taking the difference will give us angular distance.
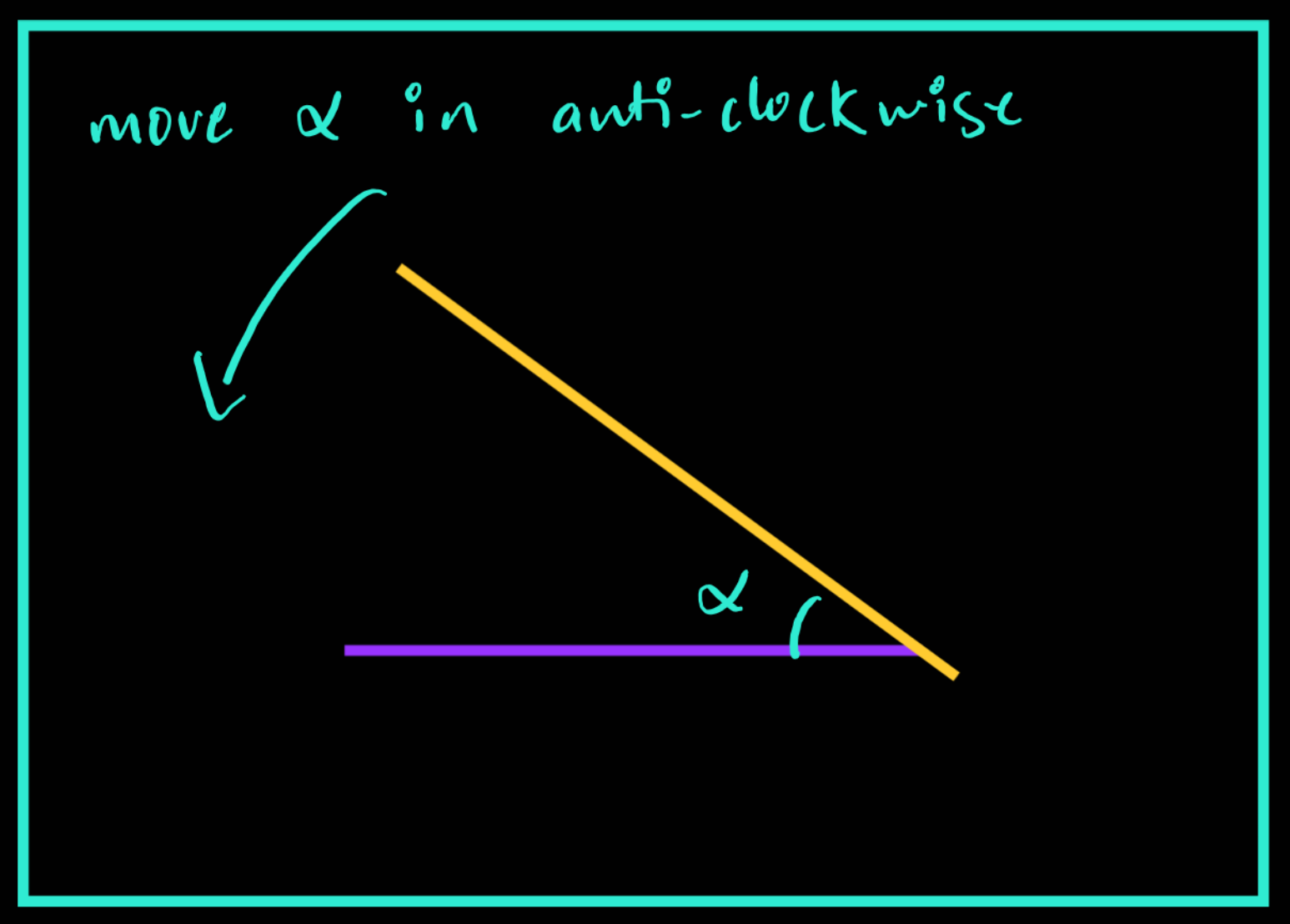
- Using
Ultrasonicsensors reading, on topic/ultrasonic_rl/scanfor left and/ultrasonic_rr/scanfor right
Doing
ros2 topic echo /ultrasonic_rl/scan --onceheader: stamp: sec: 1369 nanosec: 404000000 frame_id: ebot_base_link radiation_type: 0 field_of_view: 0.26179999113082886 min_range: 0.029999999329447746 max_range: 4.099999904632568 range: 1.163640022277832 <<<--- Here is the range we need!Using the readings from both sensors, you can find the equation of Line A and you already know the equation of Line B
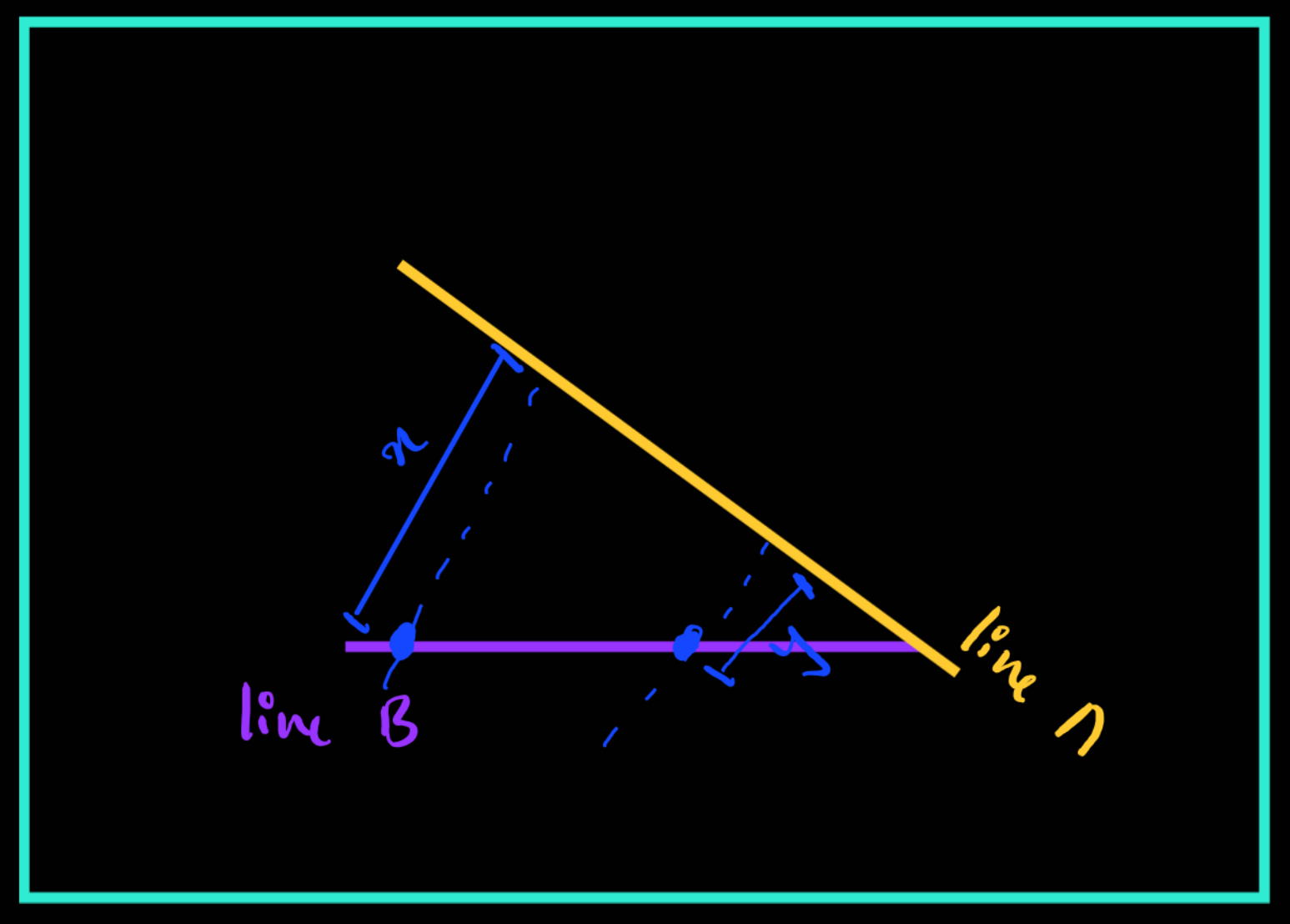
- Using IMU directly, the orientation data of the ebot can be directly accessed using topic
-
Aligning Distance: We can do this using the
Ultrasonicsensors reading to find the rear distance and keep moving back, Easy PIsy !!
Steps
-
We have provided a sample custom service msg pkg under
ebot_docking/srv/DockSw, either you can use it or else you can make your custom service msg pkg for this.### Request bool linear_dock >> Linear Correction bool orientation_dock >> Angular Correction float64 distance >> Optional param for distance float64 orientation >> Goal Orientation string rack_no >> Rack number --- ### Response bool success # indicates successful run of triggered service string message # informational, e.g. for error messages -
Make a Docking service using the above pkg, which will be docking the bot using the above methods
-
A boilerplate is been provided in the latest repo, under
ebot_docking/scripts/ebot_docking_boilerplate.py -
In the boilerplate, you have to write the controller logic for docking. Here, for example, the P-Controller is feasible and easy. What is P-Controller, go explore the internet for this and learn.
-
To write ros2 service server and client refer here.
